Displacement Sensor(Linear Variable Differential Transformer)


The model LVDT displacement sensor/crack meter is a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) type displacement sensor, which can be used for automatic detection of displacement. It has the characteristics of high precision, good stability, and strong anti-interference ability.The sensor uses 304 stainless steel metal shell, which can work in harsh environments such as humidity and dust. It is mainly used for long-term monitoring of displacement, cracks or joints for railways, highways,bridges and civil buildings, tunnels, hydropower and hydraulic engineering.
Overview
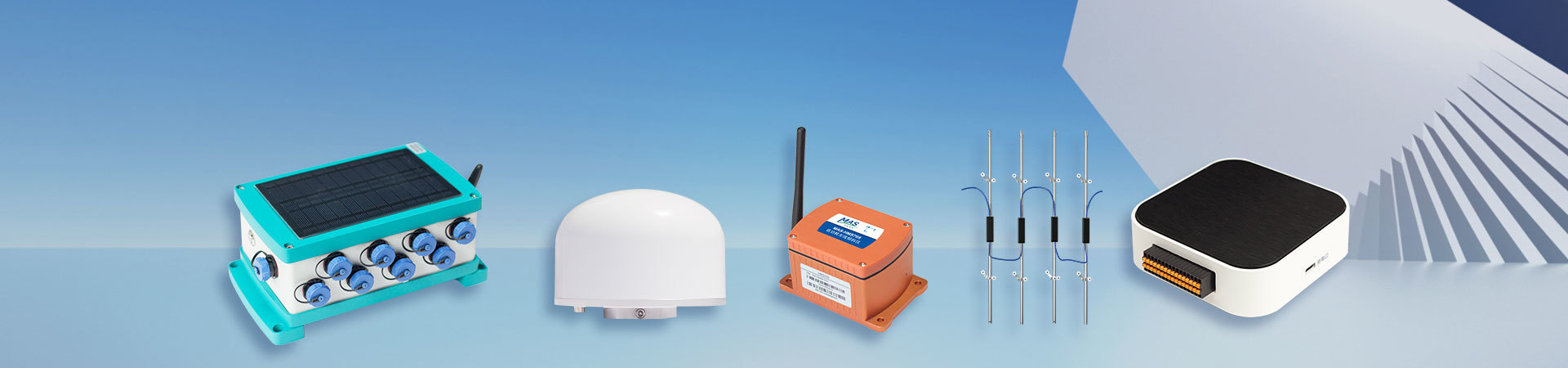
The core part of the differential transformer displacement sensor is composed of a tie rod, an iron core, a set of primary coils, two sets of secondary coils, an inner tube, and an outer tube. As the core moves within the coil, a differential voltage is generated between the two secondary coils. The voltage generated by the secondary coil is processed by detection, subtraction, filtering, zero adjustment, amplification, etc., and outputs a voltage or current signal corresponding to the movement of the iron core. When the iron core is in the middle position, the output voltage is zero. As the pull rod is pulled outward or compressed inward, the output voltage gradually increases and changes linearly with the displacement. The iron core continues to move outward, and the output voltage continues to increase. Large but no longer linear with the displacement, then the sensor enters the nonlinear region. Therefore, the movement of the iron core near the middle part is a linear region, and the movement close to the two ends of the coil is a nonlinear region. In the linear region, the displacement of the iron core has a linear relationship with the output power (voltage or current). There is still output when the iron core moves outside the linear region, but the accuracy decreases.
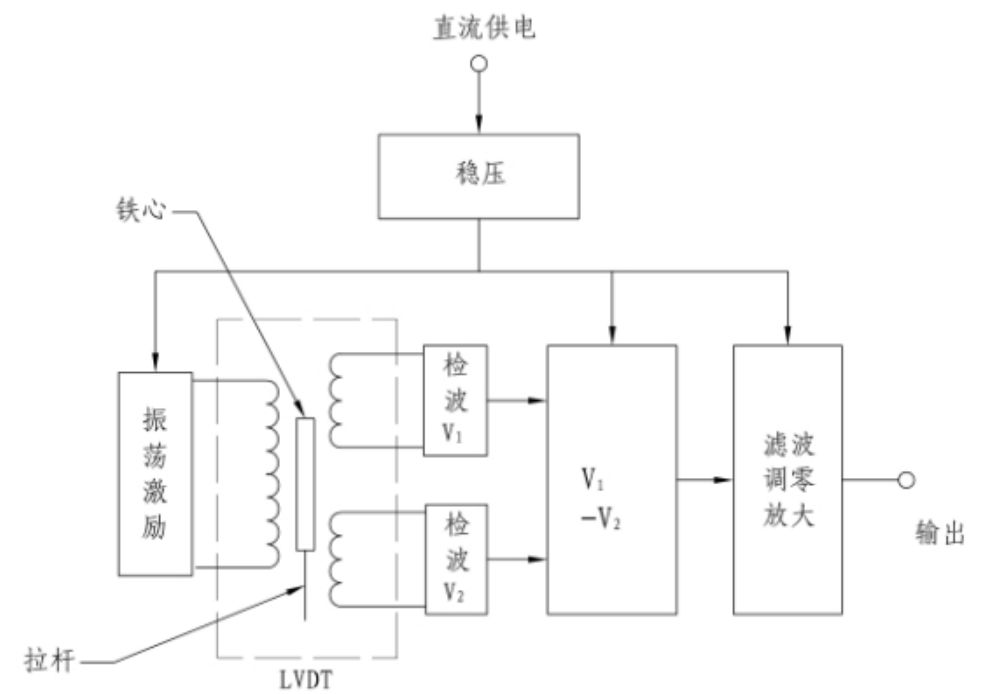
Fig.2 -1 Working principle of differential transformer displacement sensor
The relationship between the movement of the core in the coil and the output is shown in Figure 2-2. In Figure 2-2, when the iron core is in the middle position, the output voltage is zero. As the pull rod is pulled outward, the output voltage gradually increases and changes linearly with the displacement. When the iron core passes through the dotted line, the output The voltage continues to increase but no longer changes linearly with the displacement. At this time, the sensor enters the nonlinear zone. Therefore, the movement of the iron core near the middle part is a linear region, and the movement near the two ends of the coil is a non-linear region. The displacement of the iron core in the linear region is linearly related to the output power (voltage or current). The core moves outside the linear region and still has output, but accuracy is not guaranteed.
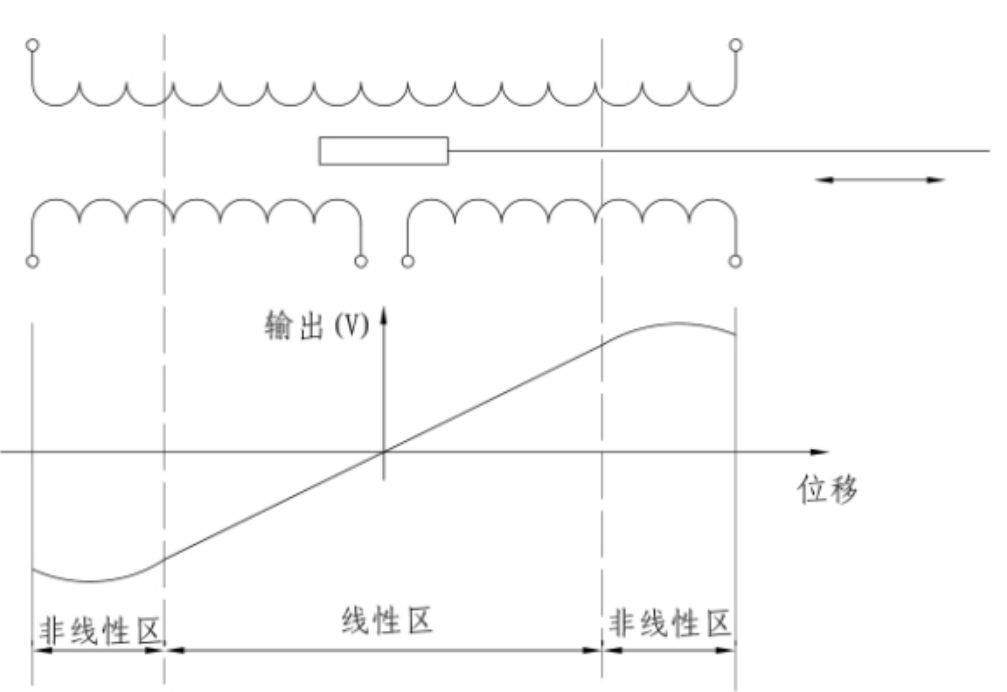
Fig. 2-2 Relationship between displacement and output of iron core
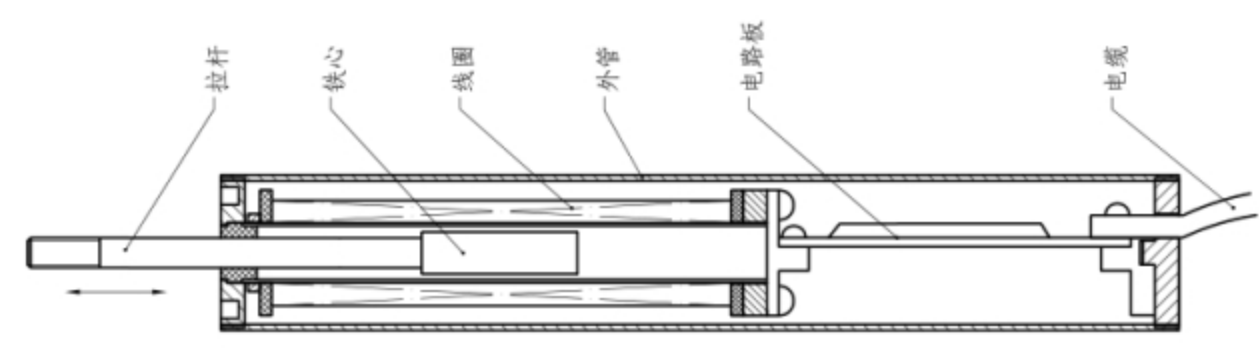
Fig. 2-3 Structure of Crack Meter
Characteristic:
- Measuring range from 10mm to 100mm, 0.1% F.S or 0.25%F.S accuracy, μm level resolution Linear Variable Differential Transformer theory Stainless steel material, corrosion resistant;
- High stability and precision;
- Temperature range from -20℃ to +85℃;
Application scenarios:
- Measuring displacement or cracks of building, bridge, tunnel, steel structures etc.
Specifications
|
Type |
LVDT-10 |
LVDT-25 |
LVDT-50 |
LVDT-100 |
LVDT-200 |
|
Measuring Range |
0~10mm |
0~25mm |
0~50mm |
0~100mm |
0~200mm |
|
Accuracy |
0.1%F.S/0.25%F.S |
0.1%F.S/0.25%F.S |
0.1%F.S/0.25%FS |
0.1%F.S/0.25%FS |
0.1%F.S/0.25%FS |
|
Resolution |
0.2μ |
0.4μ |
0.8μ |
1.6μ |
3.0μ |
|
Repeat Error |
≤0.01% ofFS |
||||
|
Temperature Range |
-20℃~+85℃ |
||||
|
Temperature Characteristics |
Zero Point ≤0.01%/℃ Sensitivity ≤0.025%/℃ |
||||
|
Output |
RS485 |
||||
|
Supply Voltage |
9~12VDC |
||||
|
Size |
ø20mm*155mm |
ø20mm*235mm |
ø20mm*300mm |
ø20mm*466mm |
ø20mm*156mm |
Related Information
Request for Quote


